[Sorry, the video "The alkaline earth metals and the oxygen group" has not yet been published.]
Learning check
[Sorry, the learning check for this video has not yet been published.]
The alkaline earth metals
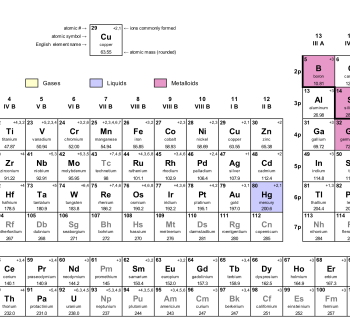
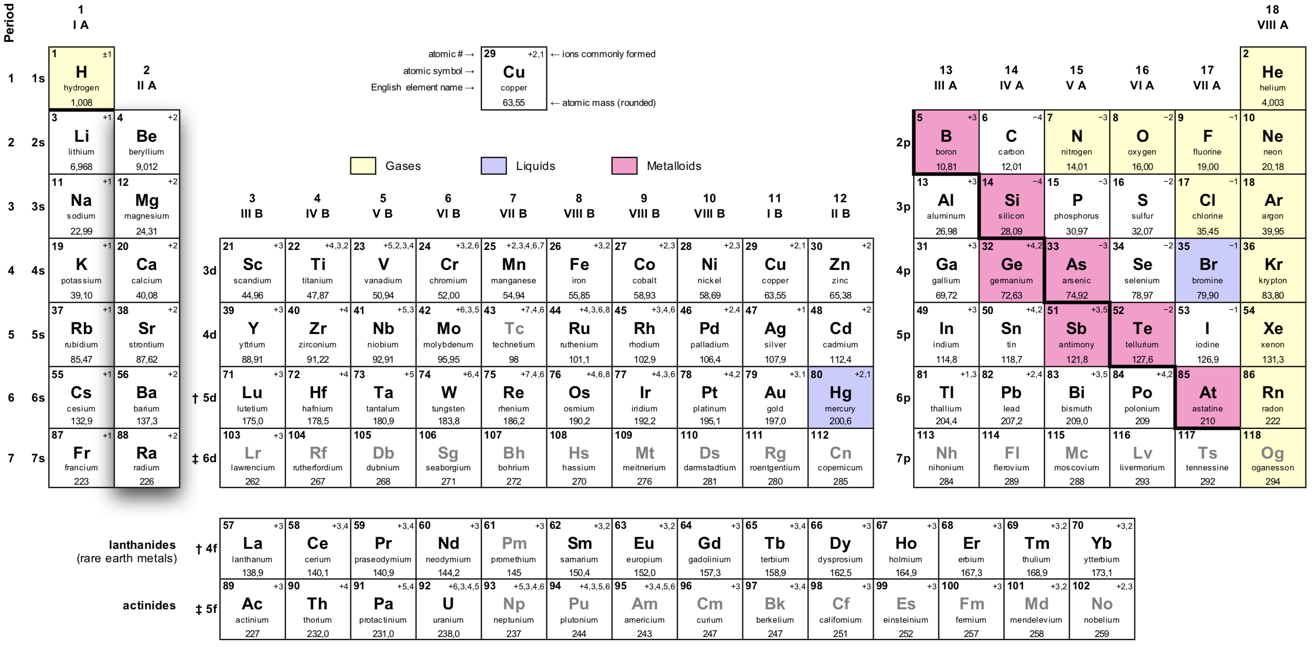 The alkaline earth metals are in group 2 of the periodic table.
The alkaline earth metals are in group 2 of the periodic table.
The alkaline earth metals are:
- Beryllium, Be
- Magnesium, Mg
- Calcium, Ca
- Strontium, Sr
- Barium, Ba
- Radium, Ra (don't confuse with radon, Rn!)
Alkaline earth metals have two valence electrons. Example: 4Be
| K | L | |
| 4p+ | 2e– | 2e– |
The most reactive alkaline earth metal
The the further away from the nucleus, the easier the valence electrons are lost.
- In radium: Valence electrons in the 5th shell ⇒ very easily lost!
- In beryllium: Valence electrons in the 2nd shell ⇒ not as easily lost ⇒ not as reactive.
The oxygen group (chalcogens)
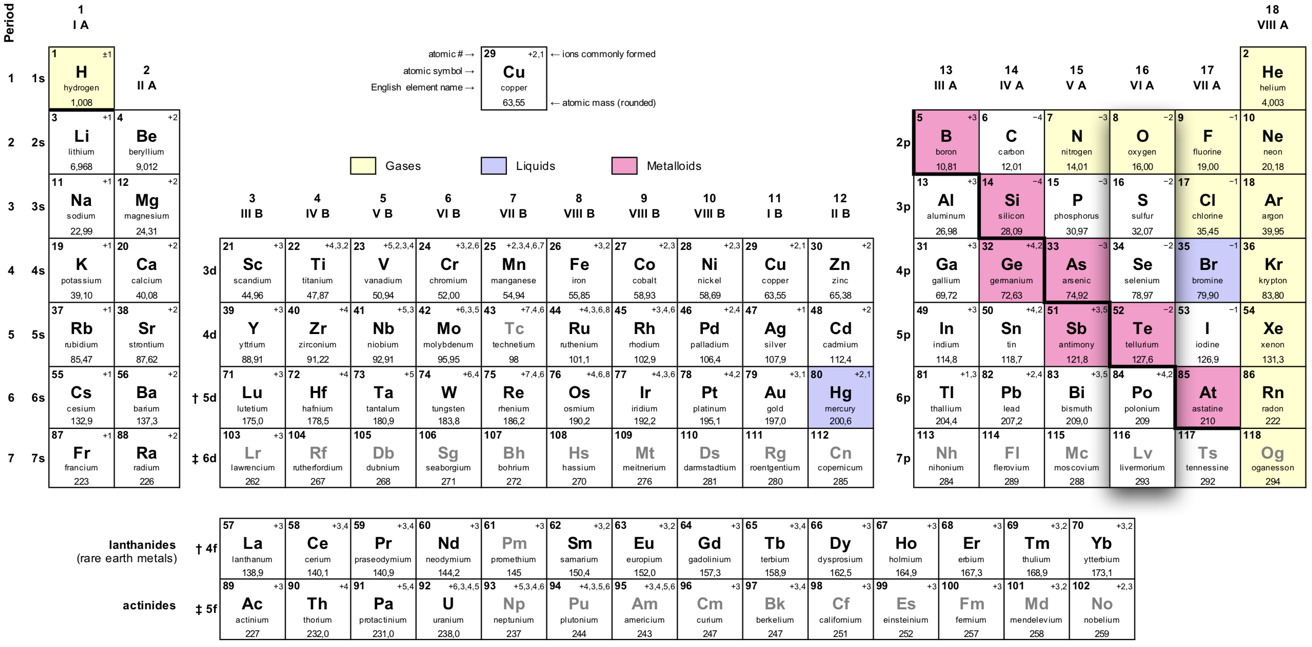 The oxygen group (the chalcogens) are in group 16 of the periodic table.
The oxygen group (the chalcogens) are in group 16 of the periodic table.
The chalcogens are:
- Oxygen, O
- Sulfur, S
- Selenium, Se
- Tellurium, Te
- Polonium, Po
- Livermorium, Lv
Chalcogens have six valence electrons. Example: 16S
| K | L | M | |
| 16p+ | 2e– | 8e– | 6e– |
The metal character increases downwards in the oxygen group
Oxygen
- Gas in room temperature, O2(g)
Sulfur
- Yellow, solid, S8
Selenium
- Non-metal, essential trace element
Tellurium
- Metalloid, used in iron alloys
Polonium
- Radioactive metal found in uranium-rich ores
Livermorium
- Synthetic. Properties: ?
Burning magnesium in air (oxygen gas)
 Magnesium burns with a white flame.
Magnesium burns with a white flame.
What happens? The magnesium is oxidized:
| + energy → |
| + 2e– |
At the same time, oxygen is reduced:
| + 2e– → |
| + energy |
Word equation:
- Magnesium + oxygen gas → magnesium oxide
Chemical equation:
- 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO