Learning check
Once you have watched the video, check your learning with this quiz.
Polar covalent bonds may cause dipoles to form
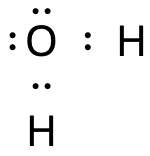
In the hydrogen chloride molecule, the bond between the hydrogen atom and the chlorine atom is polar.
- Cl is more electronegative than H
- Electrons spend more time with Cl than with H
- The molecule becomes a dipole: δ+H–Clδ–
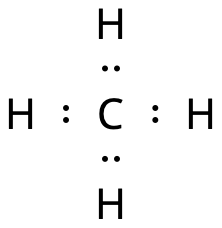
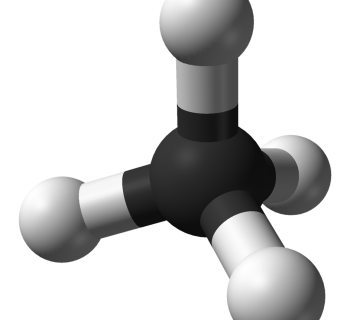
Methane, CH4, is not a dipole
The carbon and the hydrogen atoms bind to each other with electron pair bonds (covalent bonds).
- The electron pairs are as far from each other as possible.
- The electron pairs point into the corners of a tetrahedron (a triangular pyramid).
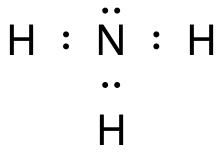
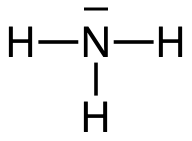
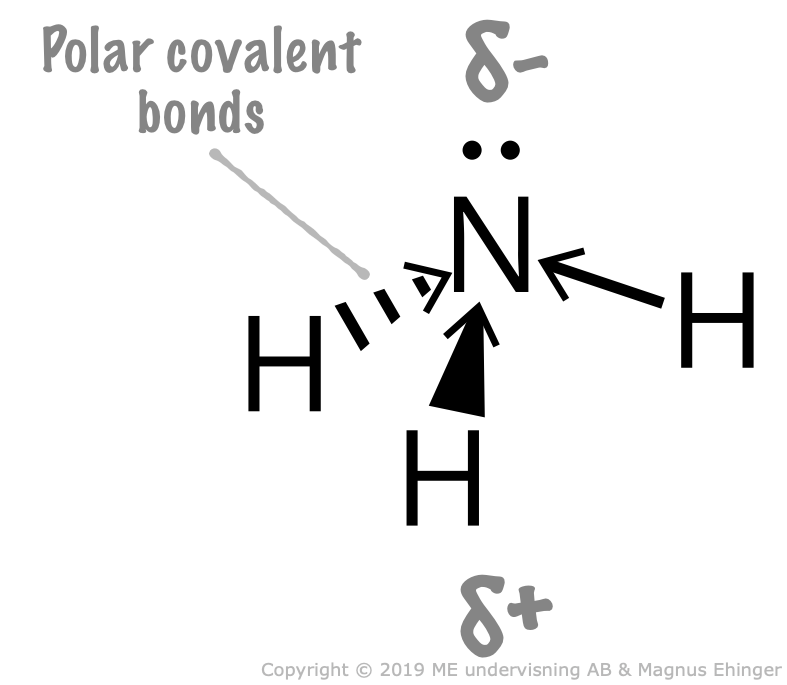
Ammonia, NH3, is a dipole
The nitrogen and the hydrogen atoms bind to each other with polar electron pair bonds (covalent bonds).
- One electron pair is non-binding ⇒ The ammonia molecule is a trigonal pyramid.
- Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen.
- The ”nitrogen end” is more negatively charged than the ”hydrogen end”.
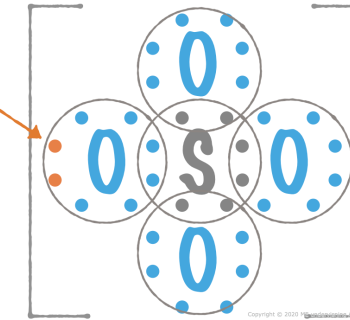
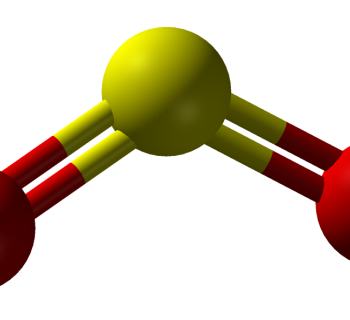
Carbon dioxide, CO2, is not a dipole
Because of the two areas with high electron density, the CO2 molecule becomes linear.
- Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon.
- One of the ”oxygen ends” is NOT more negatively charged than the other one ⇒ carbon dioxide is not a dipole.
How can you tell if a molecule is a dipole or not?
The VSEPR theory in short (explained in greater detail on this page):
- Look at the structure!
- Draw a Lewis formula.
- Count the areas with high electron density.
- Place the high-density areas as far apart from each other as possible – in 3D.
Ethylene glycol – Not necessarily a dipole, but still polar.
In the above configuration, the ethylene glycol molecule is not a dipole, because the positive and negative charges coincide with the center of the molecule.
It is, however, polar.
- The OH groups make the molecule polar.
- NHx groups also make molecules polar.