Learning check
Once you have watched the video, check your learning with this quiz.
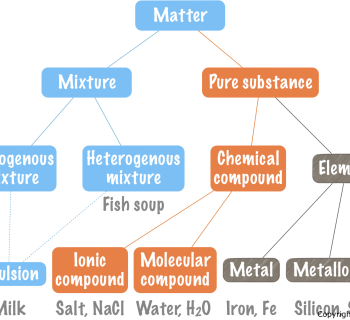
Chemistry: The study of matter and how it changes
What is matter?
- Anything that has a mass.
- [Anything you can touch, see, or see in an instrument (e.g. a telescope or a microscope).]
Examples
- Iron
- Wood
- Air
- Water
- Plastic
How does matter change? Examples:
- Ice melts
- Iron corrodes
- Children grow
- Plants grow
- Petrol burns
- … and much, much more!
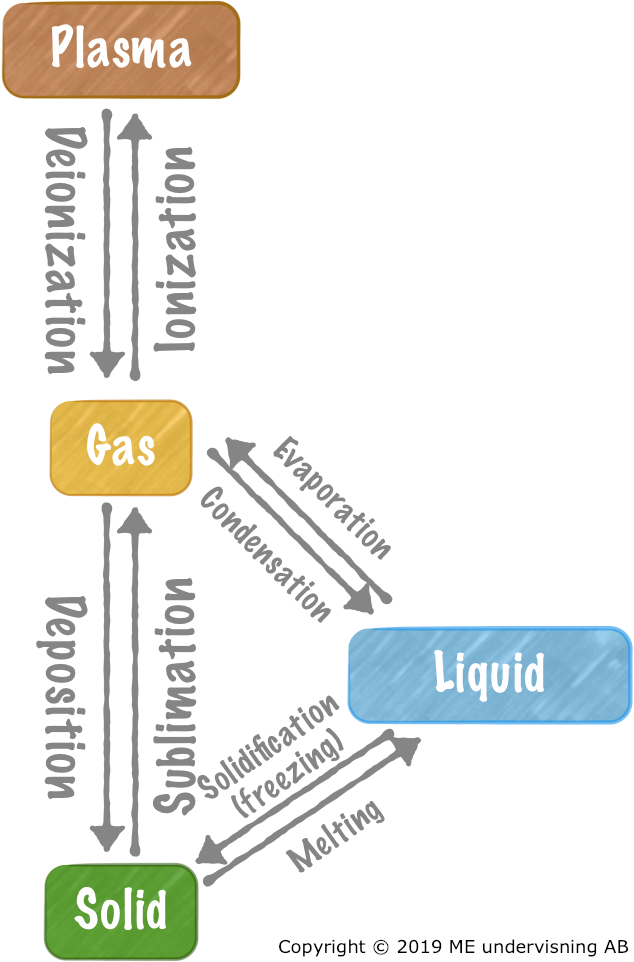
Phase transitions
Melting & solidification (freezing)
Ice melts:
- Solid water, H2O(s), with energy added gives liquid water, H2O(l).
- H2O(s) + energy → H2O(l)
Water freezes:
- Liquid water, H2O(l) freezes and forms solid water (ice), H2O(s). At the same time, energy is released.
- H2O(l) → H2O(s) + energy
Evaporation & condensation
Liquid water evaporates:
- Liquid water, H2O(l), with energy added gives water vapor, H2O(g)
- H2O(l) + energy → H2O(g)
Water vapor condenses:
- Water vaper condenses into liquid water. At the same time, energy is released.
- H2O(g) → H2O(l) + energy
Sublimation & deposition
Matter passes from solid to gas without passing liquid state.
Example: Solid iodine, I2(s), sublimates with added energy, and forms iodine vapor, I2(g).
- I2(s) + energy → I2(g)


_02.jpg)