Learning check
Once you have watched the video, check your learning with this quiz.
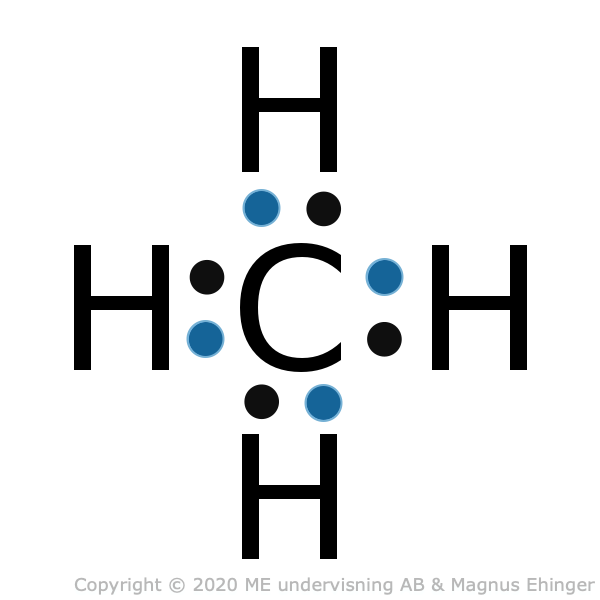
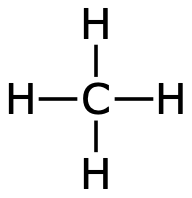
Carbon binds with covalent bonds to other atoms
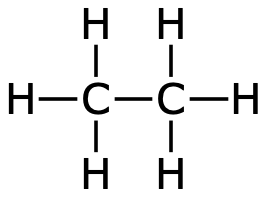
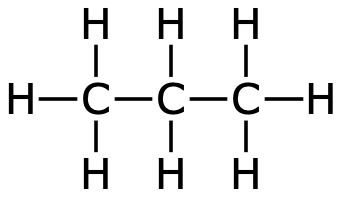
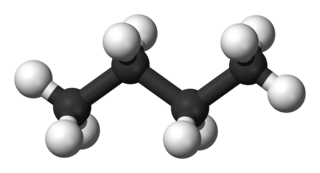
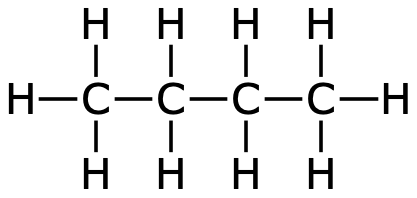
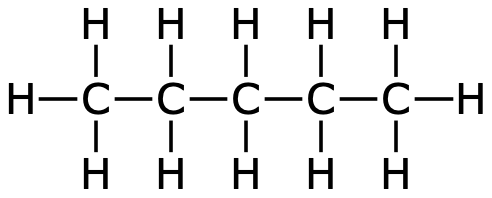
Even larger hydrocarbons
In a skeletal formula, the structure is simplified even more. Every line is a bond, and in every corner, there is a carbon atom. Everywhere where there's room, it is understood that there are hydrogen atoms.
| Name | Model | Skeletal formula | Molecular formula |
| n-hexane |  | C6H14 | |
| n-heptane |  | C7H16 | |
| n-octane | C8H18 | ||
| n-nonane | C9H20 | ||
| n-decane | C10H22 |
Cycloalkanes
Carbon atoms joined in a circular structure.
| Name | Model | Structure | Molecular formula |
| Cyclopropane |  | 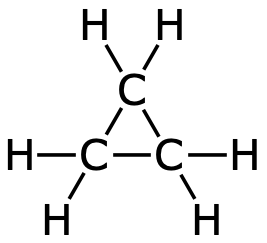 | C3H6 |
| Cyclobutane |  | 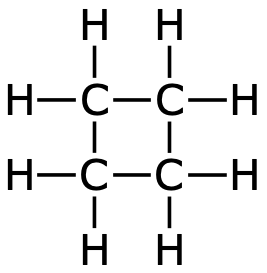 | C4H8 |
| Cyclopentane | 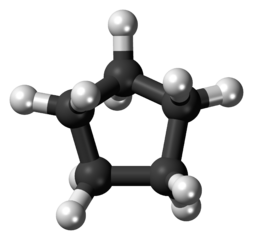 | 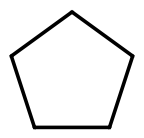 | C5H10 |
| Cyclohexane | 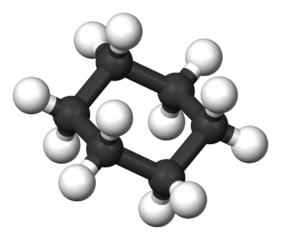 | 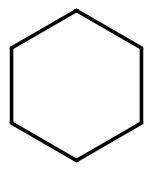 | C6H12 |
Cyclopropane and cyclobutane are both unstasble. This is because the binding angles differ a lot from 109°.
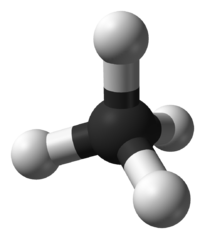
- In methane, binding angles are 109°.
- The hydrogen atoms end up in the corners of a tetrahedron.